Risk report
Risk strategy
The business activities of the KION Group necessarily involve risk. Dealing responsibly with risk and managing it in a comprehensive manner is an important element of corporate management. The overarching aim is to fully harness business opportunities while ensuring that risk always remains under control. Using its groupwide risk management system, the KION Group contains all identified risks by implementing suitable measures and takes appropriate precautions. This ensures that the losses expected if these risks arise will be largely covered and therefore will not jeopardise the Company’s continuation as a going concern.
Risk management is embedded in the corporate controlling function and plays an active and wide-ranging role due to the strategic focus of corporate controlling. The Operating Units’ business models, strategic perspectives and specific plans of action are examined systematically. This ensures that risk management is fully integrated into the KION Group’s overall planning and reporting process.
Principles of risk management
The procedures governing the KION Group’s risk management activities are laid down in internal risk guidelines. For certain types of risk, such as financial risk or risks arising from financial services, the relevant departments also have guidelines that are specifically geared to these matters and describe how to deal with inherent risks. Risk management is organised in such a way that it directly reflects the structure of the Group itself. Consequently, risk officers supported by risk managers have been appointed for each company and each division. A central Group risk manager is responsible for the implementation of risk management processes in line with procedures throughout the Group. His or her remit includes the definition and implementation of standards to ensure that risks are captured and evaluated.
The risk management process is organised on a decentralised basis. Firstly, a groupwide risk catalogue is used to capture the risks attaching to each company. Each risk must be captured individually. If the losses caused by a specific risk or the likelihood of this risk occurring exceed a defined limit, the KION Group’s Executive Board and its corporate controlling function are notified immediately. Each risk is documented in an internet-based reporting system designed specifically for the requirements of risk management. Risks affecting more than one Group company, such as market risks, competition risks, financial risks and risks arising from financial services, are not recorded individually but are instead evaluated at Group level. Consequently, such risks are not quantified.
The scope of consolidation for risk management purposes is the same as the scope of consolidation for the consolidated financial statements. The risks reported by the individual companies are combined to form divisional risk reports as part of a rigorous reporting process. To this end, minuted risk management meetings are held once a quarter. Moreover, material risks are discussed with the segments at the business review meetings. The divisional risk reports are then used to compile an aggregate risk portfolio for the KION Group as a whole. To support this, the relevant departments of the holding company are consulted each quarter in order to identify and assess risk – particularly Company-wide, cross-brand risk affecting areas such as treasury, purchasing, tax, human resources and financial services. The Executive Board of KION GROUP AG and the Supervisory Board’s Audit Committee are informed of the Group’s risk position once a quarter. The Internal Audit department audits the risk management system at regular intervals.
Material features of the internal control and risk management system pertaining to the (Group) accounting process
Principles
The main objectives of the accounting-related internal control system are to avoid the risk of material misstatements in financial reporting, to identify material mismeasurement and to ensure compliance with the applicable regulations and internal instructions. This includes verifying that the consolidated financial statements and combined management report comply with the relevant accounting standards.
Material processes and controls in the (Group) accounting process
For its (Group) accounting process, the KION Group has defined suitable structures and processes within its internal control and risk management system and implemented them in the organisation.
Changes to the law, accounting standards and other pronouncements are continually analysed with regard to their relevance and effect on the consolidated financial statements and group management report; the relevant changes are then incorporated into the Group’s internal policies and systems.
All consolidated entities must follow the KION GROUP IFRS Accounting Manual when preparing their IFRS reporting packages. This manual contains the recognition, measurement and disclosure rules to be applied in the KION Group’s accounting in accordance with IFRS. The accounting guidelines primarily explain the financial reporting principles specific to the KION Group’s business. In addition, all companies must adhere to the schedule defined by head office for preparing the consolidated financial statements and group management report.
The accounting-based internal control and risk management system encompasses defined control mechanisms, automated and manual reconciliation processes, separation of functions, the double-checking principle and adherence to policies and instructions.
The employees involved in the (Group) accounting process receive regular training in this field. Throughout the accounting process, the local companies are supported by central points of contact. The consolidated accounts are drawn up centrally using data from the consolidated subsidiaries. A consolidation department with specially trained employees carries out the consolidation activities, reconciliations and monitoring of the stipulated deadlines and processes. Monthly checklists have been drawn up for the consolidation process and are worked through in a standardised manner. All postings are managed centrally and documented. This team also monitors the system-based controls and supplements them with manual checks. The entire accounting process contains a number of specific approval stages, for which extensive plausibility checks have been set up. Employees with the relevant expertise provide support on specialist questions and complex issues.
Internal control mechanisms and ongoing analysis of the regulatory framework enable any risks that might jeopardise the compliance of the consolidated financial statements and group management report with accounting standards to be identified as soon as possible so that appropriate countermeasures can be taken. Such risks form part of the KION Group’s aggregate risk profile and are classified as operational risk.
The Internal Audit department evaluates governance, risk management and the control processes by following a systematic and structured process, thus helping to bring about improvements. It focuses primarily on the following aspects:
- appropriateness and effectiveness of the internal control systems for avoiding financial losses
- compliance with legal requirements, directives from the Executive Board, other policies and internal instructions
- correct performance of tasks and compliance with business principles
Risk
Aggregate risk
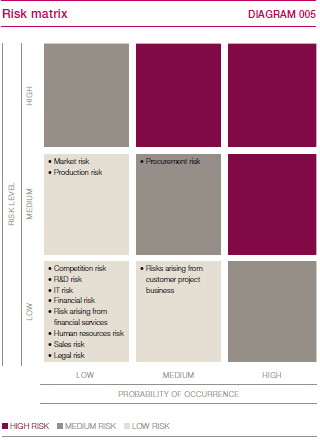
The aggregate risk position was largely unchanged compared with the end of 2016. With regard to 2018, the risks in the risk matrix below will be continually observed and evaluated in terms of their extent and probability of occurrence. For example, the KION Group considers the probability of market risk materialising as low because of the generally positive market expectations. However, the possible impact of market risk continues to be rated at a medium risk level because of the importance of the market for the KION Group’s business situation and financial performance. As things stand at present, there are no indications of any risks that could jeopardise the Company’s continuation as a going concern. > DIAGRAM 005
The market risks and competition risks described, the risks along the value chain, the human resources risks and the legal risks largely relate to the Industrial Trucks & Services and Supply Chain Solutions segments. Risks arising from financial services mainly affect the Industrial Trucks & Services segment, while financial risks would predominantly impact on the Corporate Services segment.
Market risks and competition risks
Market risks
Market risk can arise when the economy as a whole or a particular sector does not perform as well as had been anticipated in the outlook. Cyclical fluctuations in macroeconomic activity affect both the market for industrial trucks and the market for automated supply chain solutions. Customers’ decisions on whether to invest depend to a large degree on the macroeconomic situation and conditions in their particular sector. During an economic downturn, or even just periods of heightened economic uncertainty, customers tend to postpone their capital expenditure plans. Although demand for services is less cyclical, it correlates with the degree of utilisation of the trucks and systems – which usually declines during difficult economic periods. As the KION Group can only adjust its fixed costs to fluctuations in demand to a limited extent, reductions in revenue impact on earnings.
Despite the increase in the proportion of revenue generated outside the eurozone (due in part to the strong North American business of the Supply Chain Solutions segment), the bulk of revenue continues to be billed in euros. As a result, the market conditions that prevail in the eurozone impact significantly on the KION Group’s financial performance. In view of the continued stabilisation of economic growth, even – and especially – in countries that were hit hard by the financial and economic crisis, the direct market risk arising from a downturn in the economy has further reduced for the eurozone. However, any weakening of economic growth affecting major trading partners, e.g. China, might reduce eurozone customers’ willingness to invest and consequently the demand for the KION Group’s products.
Any loss of momentum in the emerging markets could also have a negative effect on global trade volumes and thus on growth in the material handling market. The market risks referred to could be heightened by geopolitical risk, including protectionist measures and possible currency crises. However, it is not currently foreseeable whether these risks will become relevant and then have a material effect on the business situation and financial performance. The geopolitical situation is monitored closely.
Various measures aimed at making cost structures more flexible – such as the consolidation of production facilities, leveraging of cost synergies and the platform strategy – help to contain the earnings risk arising from reductions in revenue caused by economic conditions. Diversification of the customer base in terms of industry and region as well as expansion of service activities also play a role in mitigating risk. Moreover, the KION Group closely monitors the market and its competitors so that it can identify market risks at an early stage and adjust its production capacities in good time. Besides global economic growth and other data, the KION Group also analyses exchange rates, price stability, the consumer and investment climate, foreign trade activity and political stability in its key sales markets, constantly monitoring the possible impact on its financial performance and financial position. Other risks arise as a result of constant changes in the Company’s political, legal and social environment. Because it operates in countries in which the political or legal situation is uncertain, the KION Group is exposed to the consequent risk of government regulation, changes to customs rules, capital controls and expropriations. The KION Group mitigates such strategic risks by, for example, carrying out in-depth market research, conducting thorough evaluation procedures to assess political and economic conditions and drafting contracts appropriately.
Competition risks
Competition risk describes the risk that growing competitive pressure will prevent the KION Group from achieving its predicted margins and market share. The markets in which the KION Group operates are characterised by strong competition, often price-driven. Price competition is compounded by some manufacturers having cost advantages in production, sometimes due to the currency situation and sometimes because local labour costs are lower. This mainly affects the Industrial Trucks & Services segment, where competition is fierce, particularly in the economy and volume price segments, and the impact is especially strong in emerging markets. Building on their local competitive strength, manufacturers in emerging markets are also looking for opportunities to expand. Although the high quality expectations and service needs of customers in developed markets present a barrier to growth for many of these manufacturers, this situation is likely to intensify competitive pressures in future.
It is also conceivable that competitors will join forces and their resulting stronger position will be detrimental to the KION Group’s sales opportunities. Moreover, predictions of higher volumes and margins may lead to overcapacity, which would put increased pressure on prices.
Although the excellent customer benefits provided by its products have enabled the KION Group to charge appropriate prices until now, it is taking a variety of steps to contain competition risk. Alliances, partnerships, acquisitions and other measures are increasingly playing a role in improving the KION Group’s competitiveness in terms of resources, market access and product range. The steps that the KION Group is taking to mitigate its competition risk also include making its plants more efficient and securing low-cost sources of supply.
The KION Group also continually evaluates its options for strengthening and consolidating its position in emerging markets, in particular through proactive cross-selling by the two operating segments, strategic partnerships, the creation of joint ventures or acquisition of local manufacturers. One of the risks of such alliances and acquisitions is that the expected benefits will materialise only partly or not at all. For example, the organisational integration of new units can harm financial performance for a variety of reasons. It is also possible that a partner will collaborate with competitors if exclusivity agreements are not in place.
Risks along the value chain
Research and development risks
The KION Group’s market position and business performance depend to a large extent on its ability to build on its leading technological position in respect of individual products and system solutions in order to become the leading supplier of automated supply chain solutions and mobile automation solutions. This requires the Group to continually develop products that meet customer expectations and comply with changing regulatory and technological requirements. To this end, the KION Group must anticipate customers’ needs and changing market conditions – including the growing use of digital technologies in value chains – and has to quickly bring new products to market. If the Company does not succeed in doing this, its technological and competitive position could be compromised in the long term.
The innovations developed by the KION Group are comprehensively protected by intellectual property rights, in particular patents. Nevertheless, there is always the possibility that products or product components will be imitated. There is also a risk that patent applications will not be successful. The KION Group mitigates research and development risk by focusing firmly on customer benefit in its development of products and solutions. Customer needs are incorporated into the development process on an ongoing basis by ensuring close collaboration between sales and development units and taking account of all region-specific requirements.
Procurement risks
Procurement activities constitute a potential risk for the KION Group in terms of the general lack of availability of parts and components and the rising cost of raw materials, energy, inputs and intermediate products. In particular, restricted capacity in a tight supplier market could result in the KION Group facing backlogs in the supply of individual raw materials and components. The KION Group obtains some of its key components from a limited number of core suppliers. Key components in the Industrial Trucks & Services segment include internal combustion engines, tyres and high-performance forged and electronic parts.
The risk of supply bottlenecks – for example in the event of a shortage of raw materials or financial difficulties at core suppliers – cannot be ruled out in future. The KION Group mitigates this risk through appropriate diversification of its supplier structure in the context of a global procurement organisation. In addition, the supplier development department, which focuses on improving suppliers’ production processes, helps suppliers to ensure that their processes are cost-efficient and offer excellent quality.
Price changes present another procurement-related risk. In 2017, around 25 per cent of the cost of materials for new trucks was directly influenced by changes in commodity prices (2016: around 25 per cent). Moreover, conditions in the commodity markets typically affect component prices after a delay of three to six months. The KION Group endeavours to pass on price increases to customers but cannot always do so entirely due to market pressures.
Production risks
Production risks are largely caused by quality problems, possible disruptions to operational procedures or production downtime at individual sites. In such cases, the KION Group’s closely integrated manufacturing network presents a heightened risk to its ability to deliver goods on time. There is also a risk that structural measures and reorganisation projects will not be implemented owing to disruption of production or strikes. Delays in delivery or a rise in the number of complaints could harm the KION Group’s positioning in the price segments and sales markets that it serves and, as a result, could harm its financial situation.
To mitigate these risks, the KION Group carries out preventive maintenance, implements fire protection measures, trains its staff and builds a pool of external suppliers. The Company has taken out a commercially appropriate level of insurance cover against loss. Quality assurance is a high priority throughout the value chain and reduces possible quality-related risks arising from the products and services provided. The KION Group mitigates its quality-related risks significantly by applying rigorous quality standards to its development activities, conducting stringent controls throughout the process chain and maintaining close contact with customers and suppliers.
Risks arising from customer project business
In the customer project business, risks can arise from deviations from the schedule originally agreed with the customer, potentially leading to revenue and profit being recognised in subsequent years or, in isolated cases, contractual penalties having to be paid. Another possible risk is that the technology deviates from the promised specifications, which may result in additional completion costs. The long-term nature of individual projects can lead to cost increases over the term of the project that were not anticipated in the project costing and cannot be passed onto the customer.
To mitigate these risks in the Supply Chain Solutions segment, project management includes a comprehensive process of risk management. This involves detailed evaluation of the risks when defining the technical aspects of quotations plus financial risk provisioning based on the individual project specifications when preparing quotations. A multistage approval process based on an extensive list of criteria ensures that financial, country-specific, currency-specific and contractual risks are largely avoided.
The potential risks that may arise in the project realisation phase are analysed in every individual project using detailed continuous reviews based on the individual items of work that make up the project. This keeps potential risks to a minimum.
Sales risks
The main sales risks – besides a drop in revenue caused by market conditions – result from dependence on individual customers and sectors. For example, it is possible that customers would postpone or cancel orders during a period of economic difficulty. There have not been any significant cancellations in previous years, however. It is also conceivable that customers would face a liquidity shortfall and therefore be unable to fulfil their payment obligations immediately or even at all. Because of its customer project business, the Supply Chain Solutions segment generally has a greater dependence on individual sectors and individual customers than the Industrial Trucks & Services segment. Nevertheless, the concentration risk for the KION Group overall is still considered to be low. The business is highly diversified from a regional perspective. In addition, the KION Group supplies companies of all sizes. Experience has shown that the KION Group’s exposure to the risk of possible payment defaults is low, but this risk can be further mitigated by recovering any collateral.
IT risks
A high degree of interconnectedness between sites and with customers and other companies means that the KION Group also relies on its IT systems working flawlessly. The KION Group undertakes ongoing further development of a reliable, extendable and flexible IT system environment with the aim of countering any IT-related risks that may arise from the failure of IT systems and IT infrastructure. Internal IT resources are pooled in the cross-segment KION IT function, which has well-established processes for portfolio management and project planning and control. Independent external audits are conducted to provide additional quality assurance. Various technical and organisational measures protect the data of the KION Group and the Group companies against unauthorised access, misuse and loss. These measures include procedures to validate and log access to the Group’s infrastructure.
Financial risks
Group Treasury is responsible for ensuring that sufficient financial resources are always available for the KION Group’s international growth. The main types of financial risk managed by Group Treasury, including risks arising from funding instruments, are liquidity risk, currency risk, interest-rate risk and counterparty risk. Counterparty risk consists solely of credit risks attaching to financial institutions. Risk management procedures issued by Group Treasury stipulate how to deal with the aforementioned risks.
Non-current financial liabilities fell by €864.3 million from their level at 31 December 2016 to reach €2,024.8 million at the end of 2017. As at 31 December 2017, the main financial liabilities classified as non-current were a promissory note with a volume of €1,010.0 million plus the amount of €1,000.0 million still outstanding under the bridge loan (AFA) following substantial repayments. The unused, unrestricted SFA loan facility stood at €965.3 million as at 31 December 2017. Risk arising out of the lending and promissory note conditions that have been agreed was not regarded as material as at 31 December 2017. It relates in particular to the restrictions in respect of compliance with financial covenants and upper limits for certain transactions and in respect of the obligation to submit special regular reports. The KION Group complied with all the obligations in this regard in the reporting year. Some of the Group’s financing takes the form of floating-rate financial liabilities. Interest-rate swaps were entered into in 2017 in order to hedge the resultant interest-rate risk.
The Company generally refers to credit ratings to manage counterparty risk when depositing funds with a financial institution. The KION Group only uses derivatives to hedge underlying operational and financial transactions; they are not used for speculative purposes. It is exposed to currency risk because of the high proportion of its business conducted in currencies other than the euro. Normally, at least 75 per cent of the currency risk related to the planned operating cash flows based on liquidity planning is hedged by currency forwards in accordance with the relevant guideline. Group Treasury rigorously complies with and monitors the strict separation of functions between the front, middle and back offices. Each Group company’s liquidity planning is broken down by currency and incorporated into the KION Group’s financial planning and reporting process. Group Treasury checks the liquidity planning and uses it to determine the funding requirements of each company.
The funding terms and conditions faced by the lenders themselves (manifested, for example, in the payment of liquidity premiums on interbank lending) may result in a future shortage of lines of credit and / or increased financing costs for companies. However, the Group currently does not expect any further changes in its lines of credit or any excessive increases in margins.
Goodwill and brand names represented 38.5 per cent of total assets as at 31 December 2017 (31 December 2016: 40.1 per cent). Pursuant to IFRS, these assets are not amortised and their measurement depends, above all, on future expectations. If these future expectations are not fulfilled, there is a risk that impairment losses will have to be recognised on these assets.
The individual Group companies directly manage counterparty risks involving customers. These counterparty risks did not change significantly in 2017. Each individual Group company has established a credit management system for identifying customer-related counterparty risks at an early stage and initiating the necessary countermeasures. Analysis of the maturity structure of receivables is an integral element of monthly reporting.
Risks arising from financial services
The leasing activities of the Industrial Trucks & Services segment mean that the KION Group may be exposed to residual value risks from the marketing of trucks that are returned by the lessee at the end of a long-term lease and subsequently sold or re-leased. Residual values in the markets for used trucks are therefore constantly monitored and forecast. The KION Group regularly assesses its aggregate risk position arising from financial services.
The risks identified are immediately taken into account by the Company in the costing of new leases by recognising writedowns or valuation allowances and adjusting the residual values. Risk-mitigating factors include the demand for used trucks, which stabilises the residual values of the KION Group’s industrial trucks. In many cases, the residual values are based on remarketing agreements that transfer any residual-value risk to the leasing company. This had a positive impact on the financial results in 2017. Groupwide standards to ensure that residual values are calculated conservatively, combined with an IT system for residual-value risk management, reduce risk and provide the basis on which to create the transparency required.
The KION Group mitigates its liquidity risk and interest-rate risk attaching to financial services by ensuring that most of its transactions and funding loans have matching maturities and by constantly updating its liquidity planning. Long-term leases are primarily based on fixed-interest agreements. The credit facilities provided by various banks and an effective dunning process ensure that the Group has sufficient liquidity.
In order to exclude currency risk, the KION Group generally funds its leasing business in the local currency used in each market.
Because of low default rates, counterparty risk has not been significant to date in the Group. The KION Group has not identified any material changes between 2016 and 2017. The Group also mitigates any losses from defaults by its receipt of the proceeds from the sale of repossessed trucks. Furthermore, receivables management and credit risk management are refined on an ongoing basis. Besides the design of the business processes, these refinements also encompass the risk management and risk control processes.
Moreover, the KION Group mostly offers financial services indirectly via selected financing partners that bear the risks of the finance transaction. As far as these financial services are concerned, the KION Group bore the counterparty risk in under 3 per cent of cases (2016: 3 per cent).
Human resources risks and legal risks
The KION Group relies on having highly qualified managers and experts in key roles. If they left, it could have a long-term adverse impact on the Group’s prospects.
That is why the KION Group actively engages in HR work aimed at identifying and developing young professionals with high potential who already work for the Company and retaining them over the long term, thereby enabling succession planning for key roles across the Group. The KION Group also positions itself in the external market as an employer of choice. This will enable it to make strategic additions to its portfolio of existing staff and, in this way, avert the risk of possibly losing expertise and thereby becoming less competitive.
Any restructuring measures may result in a risk of strikes and reactions of other kinds by the workforce. As demonstrated several times in the past, this risk is contained by collaborating closely with employee representatives and, if job losses are necessary, taking comprehensive steps to ensure they are achieved with the minimum possible social impact.
The legal risks arising from the KION Group’s business are typical of those faced by any company operating in this sector. The Group companies are a party in a number of pending lawsuits in various countries. The individual companies cannot assume with any degree of certainty that they will win any of the lawsuits or that the existing risk provision in the form of insurance or provisions will be sufficient in each individual case. However, the KION Group is not expecting any of these existing legal proceedings to have a material impact on its financial position or financial performance. These lawsuits relate, among other things, to liability risks, especially as a result of legal action brought by third parties because, for example, the Company’s products were allegedly faulty or the Company allegedly failed to comply with contractual obligations. Further legal risk may arise as a result of the environmental restoration of sites that have been shut down in recent years, for example work required due to contamination. Any damage to the environment may lead to legal disputes and give rise to reputational risk.
The Company has taken measures to prevent it from incurring financial losses as a result of these risks. Although legal disputes with third parties have been insignificant both currently and in the past, the Company has a centralised reporting system to record and assist pending lawsuits. In addition to the high quality and safety standards applicable to all users of the Company’s products, with which it complies when it develops and manufactures the products, it has also taken out the usual types of insurance to cover any third-party claims. In addition, interdisciplinary teams work on the avoidance of risks arising from inadequate contractual arrangements. A further objective of this cooperation across functions is to ensure compliance with mandatory laws, regulations and contractual arrangements at all times.
Owing to the KION Group’s export focus, legal risk and reputational risk arise due to the numerous international and local export controls that apply. The Company mitigates these risks with a variety of measures. Consequently, export controls are an important part of the compliance activities carried out by the Group companies.